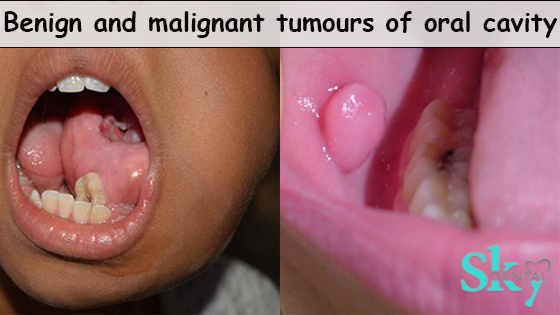
Benign and malignant tumours of the oral cavity
Benign and Malignant tumours are present in oral cavity. It’s really panicking to observe some or the other abnormalities in your oral cavity specially if you are too much engrossed in oral habits. However, the thought of cancer is very much fear-strickening to all. The statistics says that oral cancer ranks second among all other deaths due to malignancy. So Relax, let’s clear all your doubts about benign and malignant tumours.SKY
Types of tumours seen in oral cavity
There are way too many tumours that have been discovered till now that is found in the oral cavity. The most common are:
- Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma.
- Verrucous Carcinoma.
- Fibroma.( Benign)
How do you differentiate between benign and malignant tumours ?
| Benign | Malignant |
| Don’t spread to the nearby tissues, hence not alarming. | Often spread to the nearby tissue and may prove fatal. |
| Smooth and moveable in structure. | Has irregular shape and is fixed to deeper tissues. |
| Once excised doesn’t usually recur. | Recurring tendency is more. |
| For Example: Adenoma, fibroma, lipoma etc. | For Example: squamous cell carcinoma, verrucous carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma etc. |
Cause of cancerous growth in oral cavity
1. Tobacco and it’s products – One of the most common cause of malignancy of oral cavity is smoking or chewing tobacco.
2. Broken tooth or Sharp cusps due to attrition often causes a constant irritation to the tongue in cheek giving rise to epithelial abnormalities which may turn into full fledged cancer. Irritational fibroma is one of the most common benign tumours of oral cavity due to constant irritation to the cheek.
3. Excessive alcohol consumption sometimes lead to oral tumours often coupled with smoking habit.
4. However, Viruses like HPV or HIV may transform into malignancy by weakening the immune system of the body.
5. Excessive exposure to sunlight often causes tumours of lips.
6. Idiopathic or unknown reasons.
Pre malignant tumors
Therefore, there are some tumours that may or may not pose serious problems in a long run. Due to genetic changes in some cells of your body, the not so virulent tumours can transform into fatal type.
1. Carcinoma-in-situ.
2. Epithelial dysplasia.
Treatment Options:
Biopsy or histological examination of the lesion is done first as a diagnostic procedure to specify the variant of tumour, that will guide the further actions taken for treatment.
1) Excision of the mass along with the part affected with the tumour( if any). Also, Excision of affected lymph nodes of neck and complete or partial maxillectomy or mandibulectomy is done by the oral surgeon if required.
2) Radiotherapy.
3) Chemotherapy. ( Not commonly preferred).
Prevention is better than cure as per experts say. So, Leading a healthy lifestyle devoid of any sort of tobacco habits and consulting Doctors for frequent check ups is the key to combat complications.